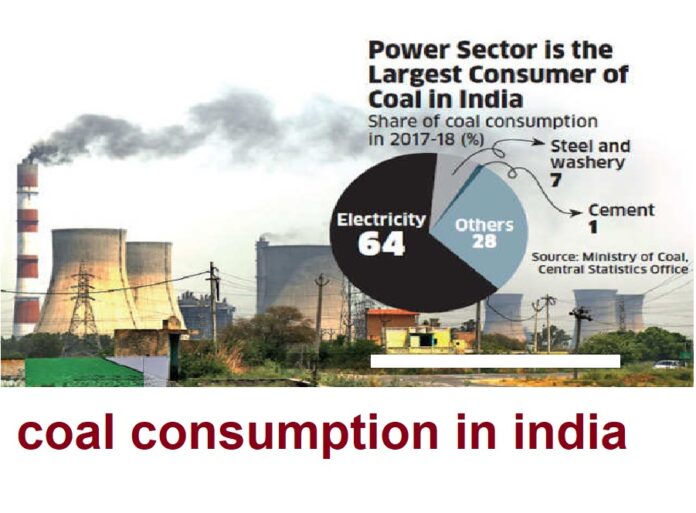
In an ever-changing energy landscape, coal remains an important component of India’s overall energy mix. The distribution of coal usage across several industries in FY 22 provides an intriguing narrative. This article goes into the facts and patterns underlying the proportion of coal consumed by various sectors in India during the fiscal year 2022.
Sector of Electricity: Illuminating Dominance (69%)
Without a question, the electrical sector is India’s greatest consumer of coal. In fiscal year 22, it accounted for a sizable 69% of total coal consumption. This large share highlights the critical role that coal continues to play in meeting India’s increasing energy demands. Despite advances in renewable energy, coal continues to be a reliable and consistent energy source for electricity generation.
Forging Ahead (6%) in the Steel Sector
In terms of coal usage, the steel industry trails the electricity sector, albeit by a wide margin. Coal is an important component of steel production, accounting for 6% of total output. Steel manufacturing processes demand a lot of energy, which corresponds to coal’s calorific value, making it an essential fuel for this industry. The steel industry aims to maintain a balance between productivity and sustainability as it continues to expand and innovate.
Building with Coal (1%) in the Cement Industry
The cement industry uses coal to power its operations in the building industry. This sector, which accounts for 1% of India’s coal consumption, is critical to the country’s infrastructural development. The use of coal in cement manufacture demonstrates its adaptability in contributing to various industrial processes. As environmental concerns mount, the sector intends to investigate greener solutions while maintaining its current growth rate.
Sponge Iron: Changing the World (1%)
Sponge iron, an important raw material in steel production, also contributes a tiny contribution to India’s coal use, accounting for 1% of total consumption. The importance of this sector in the larger steel manufacturing landscape is reflected in its reliance on coal. Sponge iron production procedures are projected to become more efficient and environmentally benign as technology progresses.
Other Sectors: A total of 23%
Aside from the major participants, different other industries contribute for 23% of coal use in FY 22. Ceramics, paper, textiles, and other industries are among them. While their individual contributions may look minor, they account for a sizable amount of coal demand. Coal’s flexibility to various industrial needs demonstrates its continuous importance.
The Importance of Coal
Finally, the distribution of coal use across different sectors in India during FY 22 offers a holistic picture of coal’s long-term importance. Coal remains relevant despite the increased emphasis on cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, from being the primary energy source for power generation to supporting steel, cement, and other industries. The balance between coal consumption and environmental concerns remains a vital part of India’s energy policy as sectors grow and technology advance.
While coal’s part of the energy mix may fluctuate in the future, its significance as a fundamental pillar in India’s industrial and energy sectors is certain to remain. This variety of coal applications highlights the versatility of coal and the ongoing need for novel ways to manage its environmental repercussions.